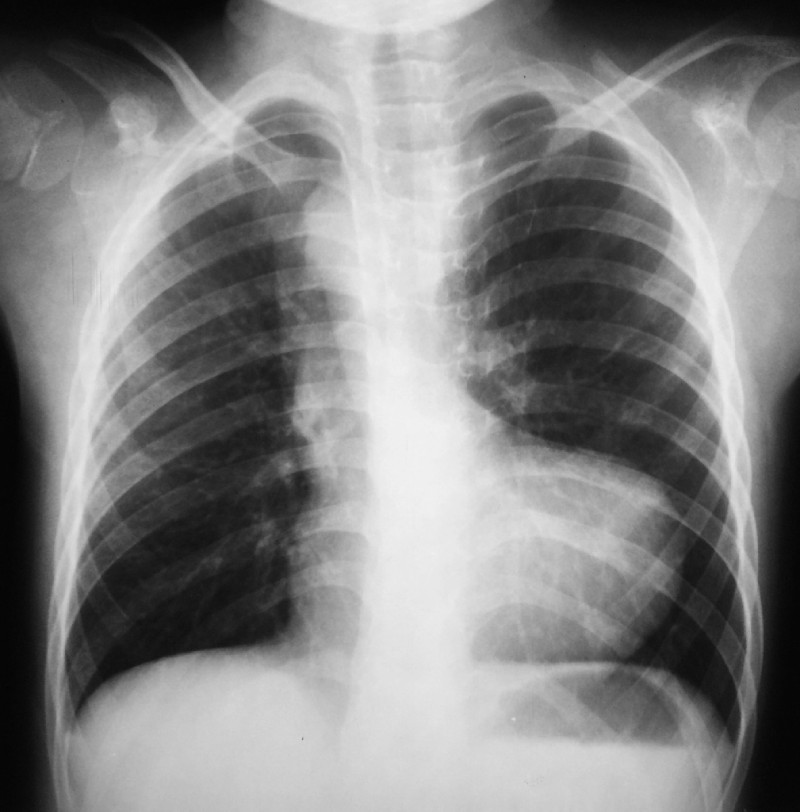
History: An infant presented in ER with respiratory distress & cyanosis. Examination shows clubbing, single S2, and ejection systolic murmur best heard in the pulmonary area. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Answer: Tetralogy of Fallot (TOF) is caused by the anterosuperior displacement of the infundibular septum. Most common cause of early childhood cyanosis.
Components: PROVe
- Pulmonary infundibular stenosis (most important determinant for prognosis)
- Right ventricular hypertrophy (RVH)—boot-shaped heart on CXR
- Overriding aorta
- VSD
Mechanism: Pulmonary stenosis forces right-to-left flow across VSD →RVH, “tet spells” (often caused by crying, fever, and exercise due to exacerbation of RV outflow obstruction).
Cause: Associated with 22q11 syndromes.
Diagnosis: CXR, ECG, Echocardiography
Treatment: Total surgical repair (The repair consists of two main steps: closure of the VSD with a patch and reconstruction of the right ventricular outflow tract). Squatting: ↑SVR, ↓right-to-left shunt, improves cyanosis.