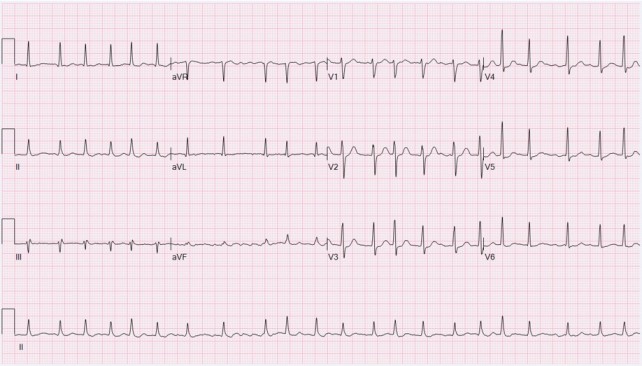
History: A 60 yr male k/c/o of HTN, Type2DM, and hyperlipidemia presents to the ER with the first episode of rapid palpitations, sob, and chest discomfort. Physical exam shows an irregularly irregular radial pulse at a rate 130 bpm, BP 110/70 mmHg, and RR 20 bpm. Heart sounds are irregular, but no third or fourth heart sound gallop or murmurs are audible. What’s the diagnosis?
Answer: Acute atrial fibrillation (AF) is a episode of a chaotic and irregular atrial arrhythmia. Prevalence increases progressively with age. AF causes significant morbidity and mortality including palpitations, dyspnea, angina, dizziness or syncope, and features of congestive heart failure, tachycardia-induced cardiomyopathy, stroke, and death. ECG shows absent P waves, presence of fibrillatory waves, and irregularly irregular QRS complexes. Treatment in hemodynamically unstable patient is DC cardioversion. In stable patient do rate control with beta-blocker and/or calcium-channel blocker +/- anticoagulation +/- electrical cardioversion or chemical cardioversion with drugs. If the precise timing of the onset of AF is unclear, a transesophageal echocardiogram must be performed to exclude left atrial clots before cardioversion.