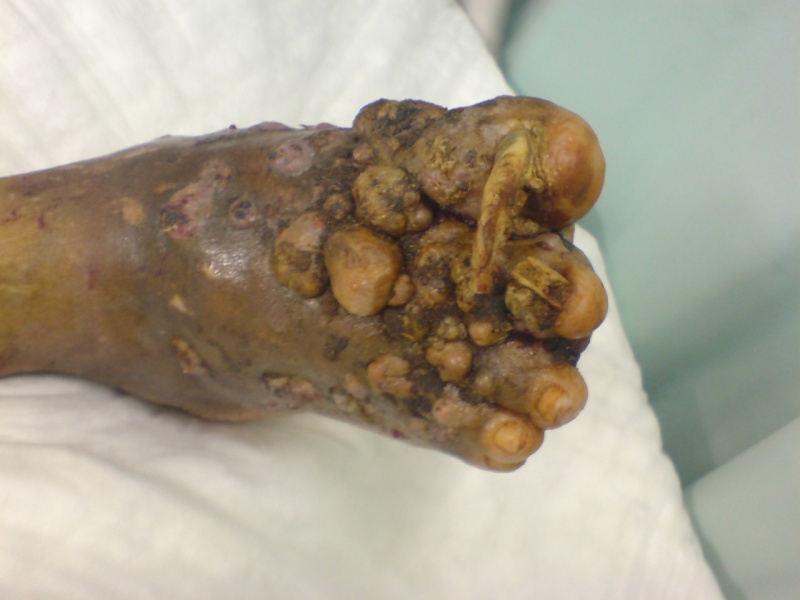
History: A 50-year-old woman with painless swelling in her left foot. The swelling started after a banal penetrating injury on the sole of her left foot 23 years ago. X-rays images showed multiple osteolytic lesions of the tarsus.
a) Eumycetoma
b) Sporotrichosis
c) Chromoblastomycosis
d) Histoplasmosis
e) Lobomycosis
Answer:
Eumycetoma, also known as Madura foot.
Causes Madurella spp., Leptosphaeria senegalensis, Curvularia lunata, Pseudallescheria spp., Neotestudina rosatii, Acremonium spp. and Fusarium spp.
Symptoms: Swelling, weeping pus filled sinuses, deformity.
Diagnostic method Microscopy, biopsy, culture, medical imaging, ELISA, immunodiffusion, DNA sequencing
Differential diagnosis: Actinomycosis (Actinomycetoma)
Treatment Surgical debridement, antifungal medicines
Medication Itraconazole, posaconazole, voriconazole
Complications: Amputation
Prognosis Recurrence is common
Frequency Endemic in Africa, India and South America