History: A crying child came with his parents to ED with c/o vomiting (nonbilious, nonprojectile), abdominal pain, he was pulling his legs to the chest, and passage of blood per rectum. On physical examination, a sausage-shaped mass was felt in RHC. What’s the diagnosis?
- Abdominal hernias
- Volvulus
- Intussusception
- Acute gastroenteritis
- Rectal prolapse
Answer: Intussusception is a medical condition in which a part of the intestine folds into the section immediately ahead of it. It typically involves the small bowel and less commonly the large bowel. MC type is Ileocecal – 77%.
Signs and symptoms:
- Early signs: Periodic abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, pulling legs to the chest area.
- Later signs: PR bleed, often with “red currant jelly” stool (stool mixed with blood and mucus), lethargy, and sausage-shaped mass.
Etiology: Infections, Anatomical factors, Altered motility, Meckel’s diverticulum, Duplication, Polyps, Appendicitis, Hyperplasia of Peyer patches or Idiopathic.
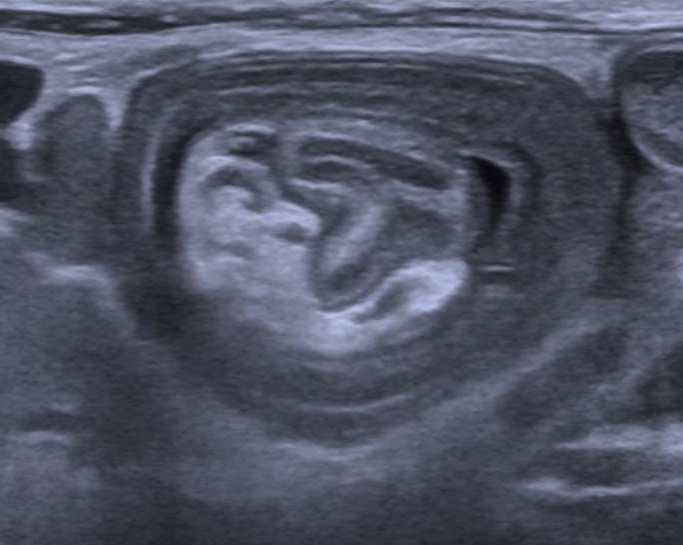
Diagnosis: USG (target or doughnut sign or pseudokidney), CT, X-ray abdomen.
Treatment: Barium or water-soluble enema, surgical reduction.