New more aggressive targets for blood pressure and lipids are among the changes to the annual American Diabetes Association (ADA) Standards of Care in Diabetes 2023. The new definition of hypertension in people with diabetes is ≥ 130 mmHg systolic or ≥ 80 mmHg diastolic blood pressure, repeated on two measurements at different times. Among individuals with established cardiovascular disease, hypertension can be diagnosed with one measurement of ≥ 180/110 mmHg. The goal of treatment is now less than 130/80 mmHg if it can be reached safely.
Investigators found that levels of formic acid, a metabolic product of formaldehyde found in urine, were significantly higher in individuals with Alzheimer disease including those with subjective cognitive decline, which may indicate very early stages of the disorder. Urinary formic acid and formaldehyde are likely to be new biomarkers independent of the existing AD diagnostic criteria. Researchers also compared formic acid and formaldehyde levels across different AD stages and found significantly higher levels across all stages compared with people who had no cognitive decline. Levels were also higher in patients with AD than in patients with MCI and those with cognitive impairment and no MCI, as well as in those with poorer neurologic test scores.
Source: Frontiers
Clinical Inshorts by ClinicHours
History: A 33-year-old man presented to the ED with low-grade fever for 3 weeks, vomiting for 1 week and anuria for 3 days. He also reported dysuria and breathlessness for 1 week. There was no history of decreased urine output, dialysis, effort intolerance, chest pain or palpitation, dyspnoea and weight loss. Family history included smoky urine in his younger brother in his childhood. Severe pallor was present with mild pedal oedema. BP 180/100 mm Hg and P 116/min regular. No evidence of jaundice, clubbing cyanosis or lymphadenopathy was found. Physical examination revealed bibasilar end-inspiratory crepitations in lungs and suprapubic tenderness. There was no hepatosplenomegaly or ascites. Cardiac examination was normal. He was found to have severe bilateral hearing loss, which was gradually progressive for 5 years. Slit-lamp examination showed bilateral anterior lentiglobus with posterior lenticonus. What’s the diagnosis?
Answer: Alport syndrome is caused by mutations in COL4A3, COL4A4, and COL4A5, three of six human genes involved in basement membrane (type IV) collagen biosynthesis.
Signs & symptoms: Hereditary nephritis, sensorineural hearing loss, retinopathy, anterior lenticonus.
Diagnosis: At least 4 of the following 10 criteria should be fulfilled:
- A family history of nephritis in a first-degree relative male linked to the index case.
- A history of persistent haematuria.
- Bilateral SNHL involving higher frequencies.
- Widespread GBM ultrastructural abnormalities.
- Ocular findings such as anterior lenticonus and retinal flecks.
- Mutation in COL4A gene.
- Immunohistochemical evidence of partial or complete loss of Alport epitope.
- Gradual progression to ESRD in at least relatives of index case.
- Macrothrombocytopenia.
- Diffuse leiomyomatosis.
Differential diagnosis: Thin basement membrane disease (TBMD), Mesangial IgA nephropathy, Drug-induced renal and ototoxicity (eg, aminoglycosides), Branchio-otorenal syndrome.
Treatment: ACE inhibitors, dialysis or transplantation.
Clinical Rounds by ClinicHours
The US FDA has approved the anti-CD3 monoclonal antibody teplizumab-mzwv (Tzield, Provention Bio) to delay the onset of clinical type 1 diabetes in people aged 8 years and older who are at high risk for developing the condition. It is administered by intravenous infusion once daily for 14 consecutive days. The specific indication is to delay the onset of stage 3 type 1 diabetes in adults and pediatric patients 8 years and older who currently have stage 2 type 1 diabetes.
Type 1 diabetes staging:
- Stage 1: Presence of beta-cell autoimmunity with two or more islet autoantibodies with normoglycemia
- Stage 2: Beta-cell autoimmunity with dysglycemia yet asymptomatic
- Stage 3: Symptomatic onset of type 1 diabetes.
Stage 2 type 1 diabetes is associated with a nearly 100% lifetime risk of progression to clinical (stage 3) type 1 diabetes and a 75% risk of developing the condition within 5 years.
Clinical Inshorts by ClinicHours
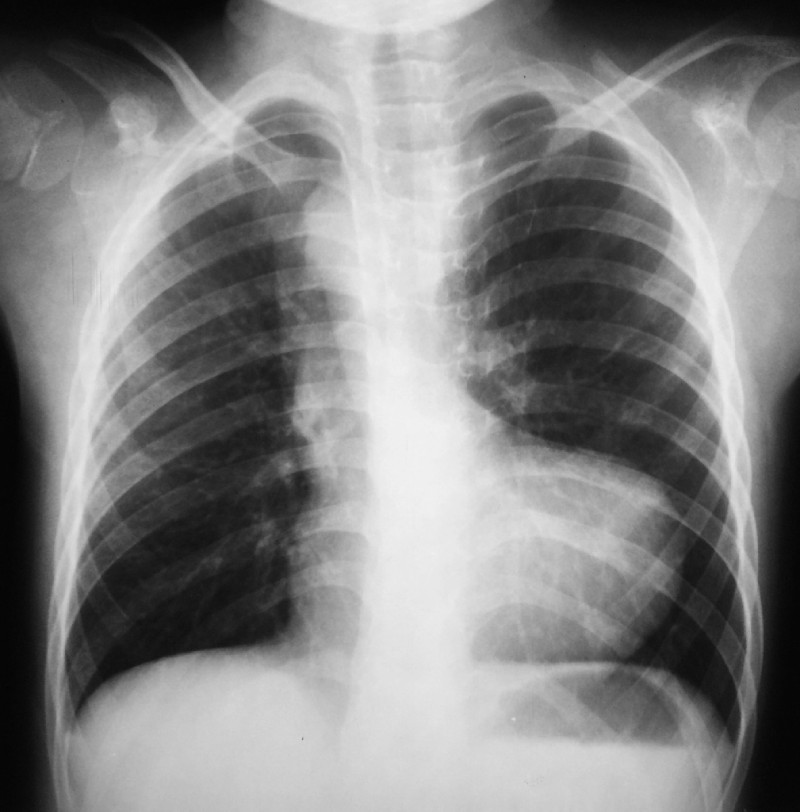
History: An infant presented in ER with respiratory distress & cyanosis. Examination shows clubbing, single S2, and ejection systolic murmur best heard in the pulmonary area. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Answer: Tetralogy of Fallot (TOF) is caused by the anterosuperior displacement of the infundibular septum. Most common cause of early childhood cyanosis.
Components: PROVe
- Pulmonary infundibular stenosis (most important determinant for prognosis)
- Right ventricular hypertrophy (RVH)—boot-shaped heart on CXR
- Overriding aorta
- VSD
Mechanism: Pulmonary stenosis forces right-to-left flow across VSD →RVH, “tet spells” (often caused by crying, fever, and exercise due to exacerbation of RV outflow obstruction).
Cause: Associated with 22q11 syndromes.
Diagnosis: CXR, ECG, Echocardiography
Treatment: Total surgical repair (The repair consists of two main steps: closure of the VSD with a patch and reconstruction of the right ventricular outflow tract). Squatting: ↑SVR, ↓right-to-left shunt, improves cyanosis.
Clinical Rounds by ClinicHours
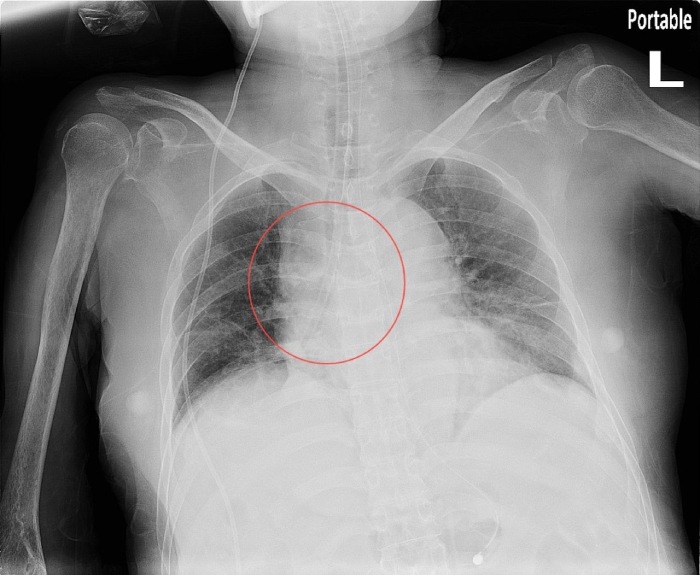
History: A 60 year old woman nursing home patient with Type2DM, HTN, and a prior haemorrhagic stroke presented to ED with progressive dyspnoea, cough with white sputum and low-grade temperature. On arrival, the patient was tachypnoeic, using accessory muscles and oxygen desaturation was noted. Physical examination showed no jugular vein engorgement, trachea was not deviated and auscultations revealed bilateral equal breath sounds with bi-basilar rales. Despite supplemental oxygen, the patient required intubation and was admitted to ICU. However, in the ICU, the patient’s saturation continued to fluctuate despite varying ventilation settings. What is the most likely cause of respiratory failure in the patient?
-
Pulmonary oedema
-
Pneumonia
-
Pneumothorax
-
Foreign body aspiration
Answer: The foreign body in the right bronchus. The foreign body was later found to be a suction tube used by the nursing home, which was suspected to have broken off at some point for unknown reason.
The ABCDEFGHI mnemonic is very useful: A stands for assessment of quality and airway. The X-ray here was a supine AP view, with poor inspiration of only six posterior rib visible, and reviewing the airway, there was no tracheal deviation, the endotracheal tube was in place but a suspicious object could be seen in the right bronchus. The rest of the mnemonic would be: B for bones and soft tissue (no bone fractures and no subcutaneous air). C for cardiac silhouette, D for diaphragm, E for effusion, F for fields, fissure and foreign body, (pneumonia, pulmonary oedema and pneumothorax) are not seen but there are three foreign bodies: the endotracheal tube, VP shunt and again, one in the right bronchus, G for gastric bubble and great vessels, H for hila and mediastinum and lastly I for impression. Using this standardised approach, we would have a greater chance of identifying the foreign body and thus provide more timely management for the patient.
Reference: BMJ
Clinical Rounds by ClinicHours
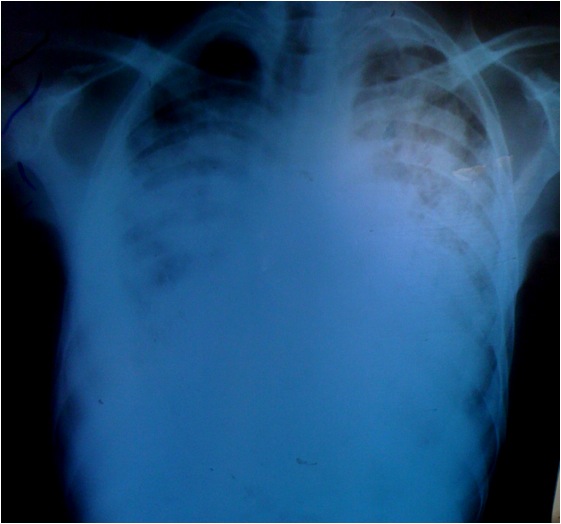
History: A 40 year old male with c\o fever, cough productive of mucoid sputum without haemoptysis and chest pain for four months. He also reported weight loss for two months and abdominal and lower limb swelling for one month. In addition he had fatigue, palpitations and exertional dyspnoea but denied orthopnoea. Chest X-ray showed a massively enlarged cardiac silhouette and bilateral pulmonary infiltrates or oedema. An urgent bedside ultrasound showed a large pericardial effusion of about 2 cm, right atrial collapse and right ventricular collapse in diastole. What’s the diagnosis?
Answer: The patient presented with cardiac tamponade, the most severe complication of TB pericarditis. Cardiac tamponade occurs when fluid in the pericardial space accumulates faster than the pericardial sac can stretch and so causes high pressure compressing the heart and preventing the heart from expanding fully. However, if the fluid accumulates more slowly as with TB pericarditis, the pericardial sac can expand to hold over one litre of fluid before critical compression arises.
Signs & Symptoms: The three classical signs of cardiac tamponade (Beck’s triad) are hypotension, jugular venous distention, and muffled heart sounds. Hypotension results from decreased cardiac output, jugular-venous distension results from impaired venous return to the heart and, muffled heart sounds are due to pericardial fluid. There are other physical signs that may indicate cardiac tamponade. On inspiration the central venous pressure (jugular venous pressure) would normally fall but with tamponade this rises. Pulsus paradoxus is the finding of a fall in the systolic blood pressure of more than 10mmHg when the patient inspires.
Causes: Infection- viral, TB, bacterial, fungal, HIV, Malignancy, Post-cardiac injury syndrome (after trauma or cardiothoracic surgery), Acute myocardial infarction (acute, delayed), Metabolic-uremia, hypothyroidism, Collagen vascular diseases- rheumatoid arthritis, lupus erythematosus, Radiation, Idiopathic.
Investigation: The chest Xray of a patient with large pericardial effusion shows a large “boot-shaped” cardiac silhouette but it can be difficult to tell if a large heart is due to dilated cardiomyopathy or pericardial effusion. Ultrasound easily detects a large pericardial effusion: the fluid appears anechoic or black around the heart. The right atrium and right ventricle appear collapsed with dilation of the inferior vena cava.
Treatment: Emergency pericardiocentesis by a subxiphoid approach using ultrasound guidance.
Clinical Rounds by ClinicHours
The US FDA has approved a new combination of immunotherapies for use together with platinum-based chemotherapy for the treatment of adults with metastatic non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) whose tumors do not have EGFR mutations or ALK aberrations. The new combination comprises two drugs that act at different immune checkpoints: the CTLA-4 inhibitor tremelimumab (Imudo) and the anti-PDL1 antibody durvalumab (Imfinzi). This combination was recently approved for the first time for use in liver cancer, and durvalumab is already approved for use in lung cancer, bladder cancer, and biliary tract cancers.
Inshorts by ClinicHours
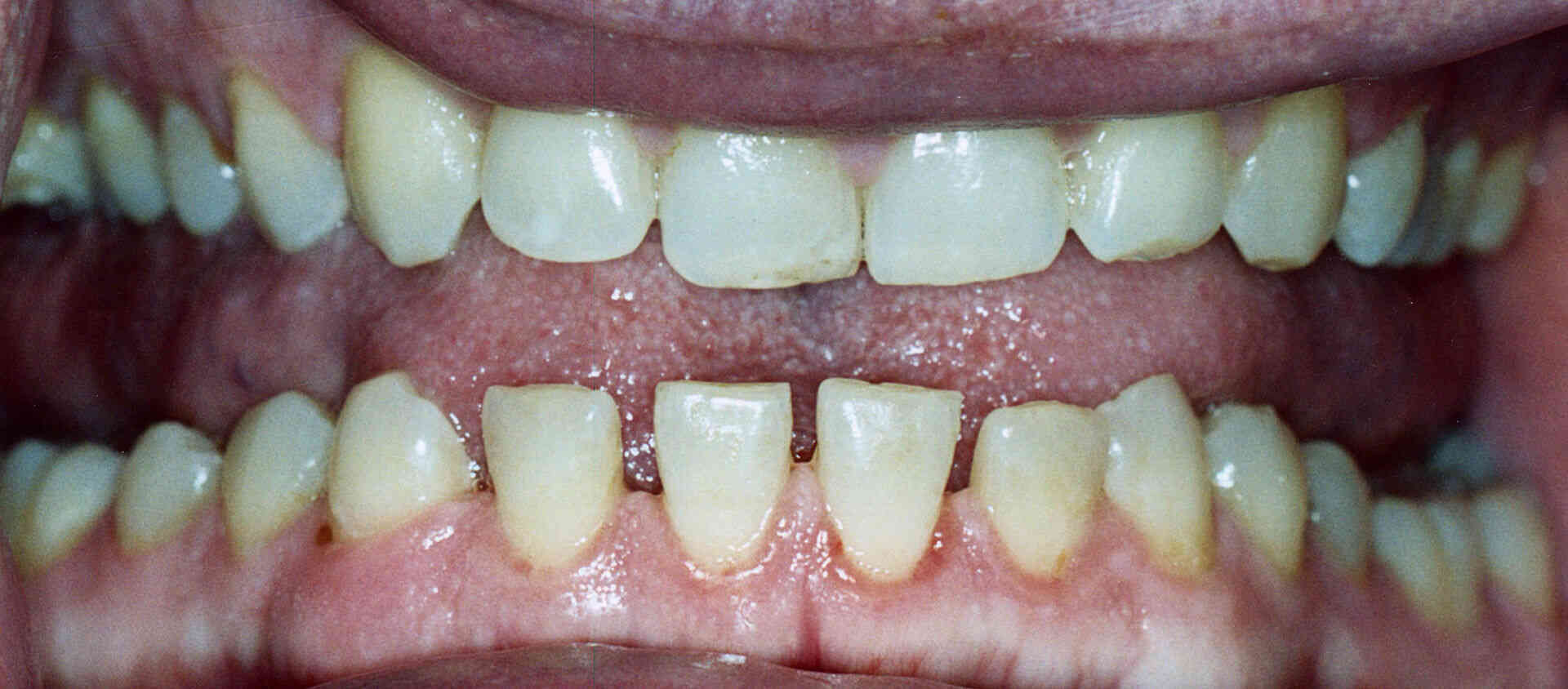
History: A 30-year-old man presented with an 11-year history of coarse facial features and progressive enlargement of hands and feet. On physical examination, his height was 1.70 m and his weight was 65 kg. Coarse facial features included enlarged frontal and nasal bone, thickened facial and scalp skin including the periorbital area, and thickened lips. His lower jaw shows the classic spacing of teeth. Funduscopic examination revealed the absence of papilloedema. Hands and feet are noted to be enlarged but non-oedematous. What’s the diagnosis?
Answer: Acromegaly is a disorder that results from excess growth hormone (GH) after the growth plates have closed.
Symptoms: The initial symptom is typically enlargement of the hands and feet. There may also be an enlargement of the forehead, jaw, and nose. Other symptoms may include joint pain, thicker skin, deepening of the voice, headaches, and problems with vision. Complications of the disease may include type 2 diabetes, sleep apnea, and high blood pressure.
Cause: Acromegaly is usually caused by the pituitary gland producing excess growth hormone due to a benign pituitary adenoma.
Diagnosis: Measuring insulin-like growth factor I in the blood. After diagnosis MRI of the pituitary is carried out to determine if an adenoma is present. If excess growth hormone is produced during childhood, the result is the condition gigantism rather than acromegaly, and it is characterized by excessive height.
Treatment: Surgery to remove the tumor, radiation therapy, somatostatin analogues or GH receptor antagonists may be used. Radiation therapy may be used if neither surgery nor medications are completely effective.
Clinical Rounds by ClinicHours
Neurofilament light chain (NfL) is a biomarker for both disease progression and treatment response in multiple sclerosis (MS), but the search continues for additional biomarkers to distinguish between disease activity and progression. Serum glial fibrillary acid protein (GFAP) could be a useful complement to NfL in MS, although it is not ready for the clinic.NfL is a structural protein of neurons, while GFAP is a structure protein of astrocytes. NfL therefore reflects neuronal damage, while GFAP is an indicator of astrogliosis and astrocytic damage. GFAP has been shown to be increased in progressive MS and has been applied in traumatic brain injury and neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder. Serum GFAP is a promising biomarker reflecting progression in MS and it is complementary to NfL.