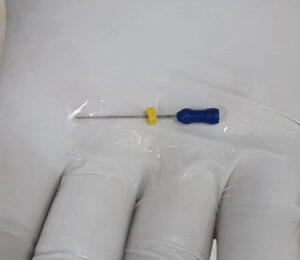
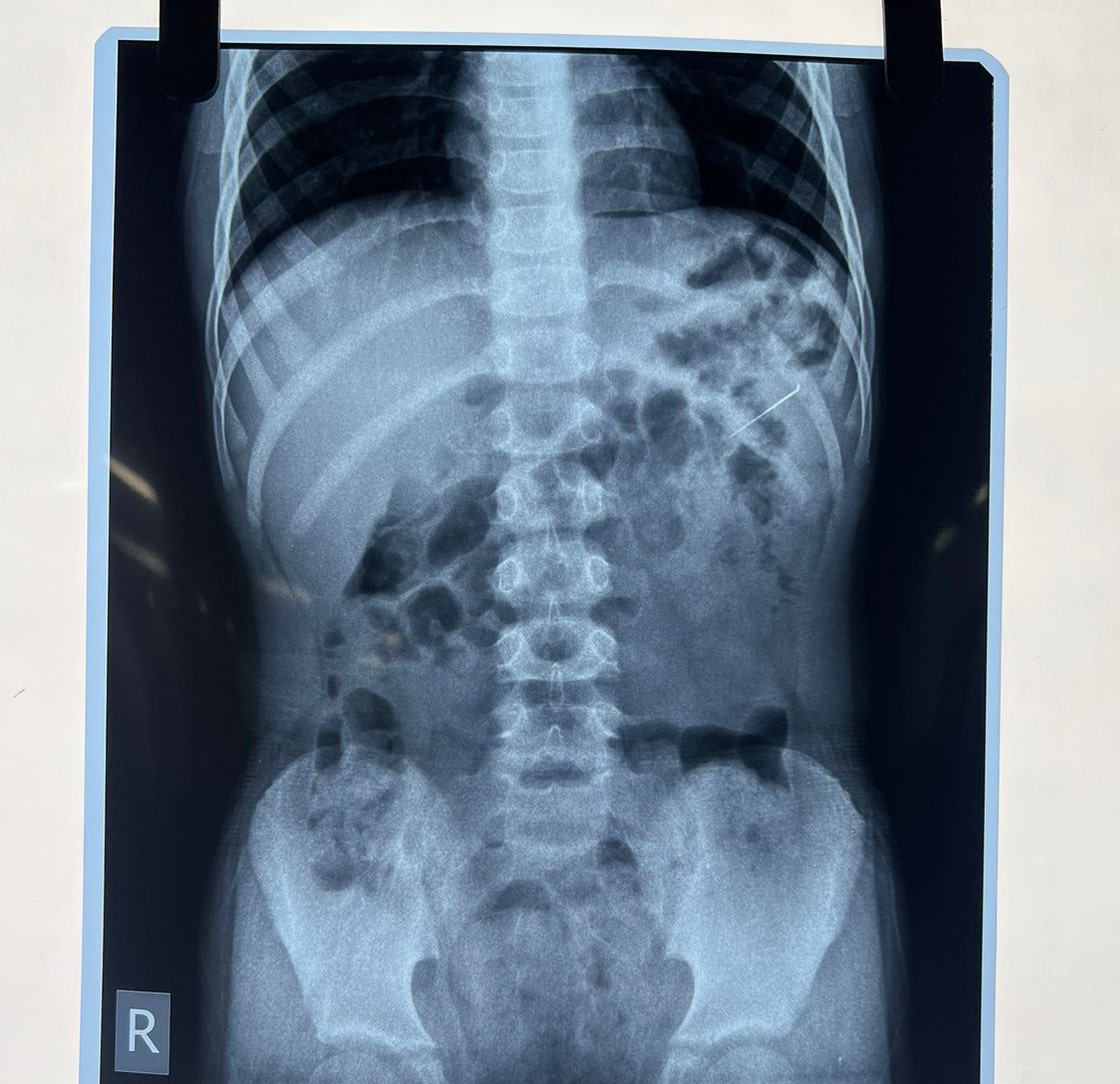
History: A 8 yr old boy came to the ED with accidental ingestion of an Endodontic file while having a dental procedure. Pt. was asymptomatic at the time of presentation with no SOB, abdominal complaints & vomiting. What’s the next step you will do in ED?
Answer: CXR -AP view & abdominal x-ray – Erect & supine was done on arrival after initial assessment. Pt. was hemodynamically stable. Pt was admitted to the surgery ward for observation. There were no signs of peritonitis or perforation. In this case, FB passed spontaneously with the stool on its own & no surgical intervention was required.
Foreign body ingestion is a common clinical problem. Commonly seen in children, older people, people with intellectual disability, psychiatric pathologies & prisoners/inmates.
Most ingested foreign bodies will pass through GI tract without symptoms & cause only minor mucosal injury. However, 10% – 20% of cases will require non-operative intervention, 1% may develop complications (e.g. bowel obstruction, perforation, severe hemorrhage, abscess formation, or septicemia) & require surgical interventions.
Look for dysphagia, abdominal pain, signs of peritonitis, stridor, wheezing, gagging, nausea/vomiting, neck/throat pain, atypical chest pain or non-cardiac chest pain, choking & LGIB.
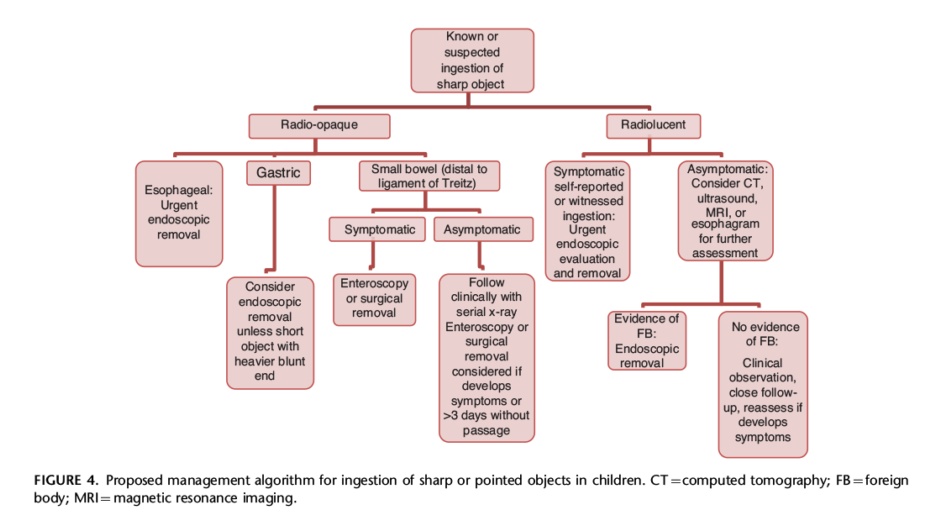
Endoscopy is the first-line intervention for the removal of FB. However, Button battery ingestion can be potentially fatal and thus requires immediate intervention. Check out the management algorithm for sharp FB ingestion.


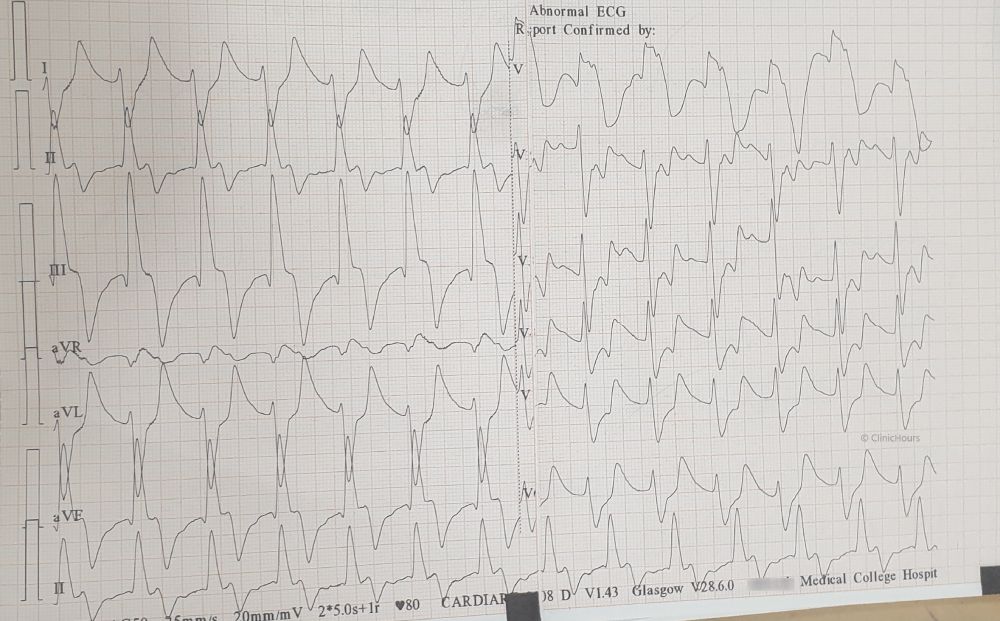
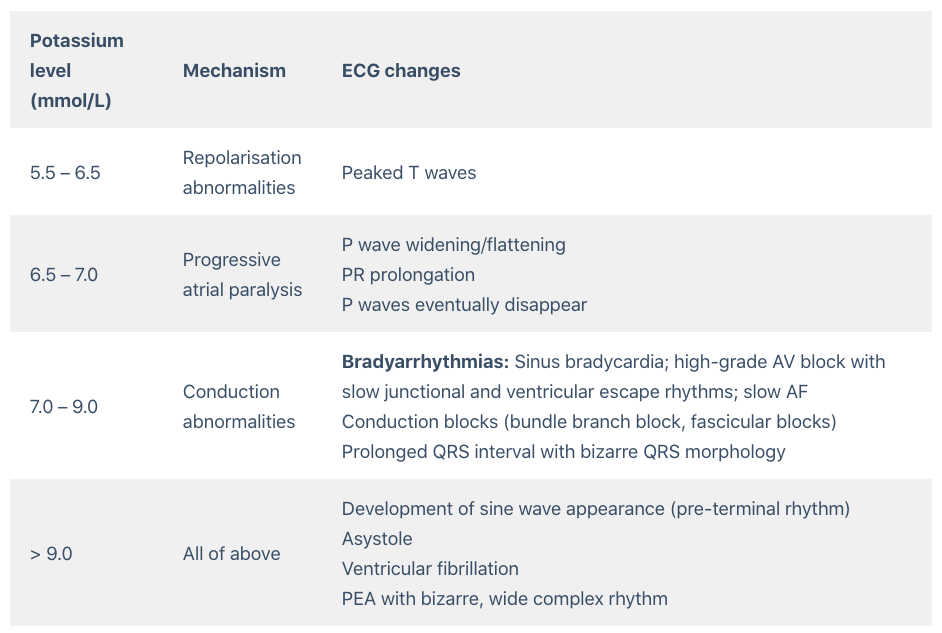 The patient was treated with 10% 10ml of IV calcium gluconate, nebulised with Salbutamol, 10 units of regular insulin IV combined with dextrose 50%, IV sodium bicarbonate 50 mEq and Inj. Furosemide 40mg IV. Emergent haemodialysis was initiated. Pt was shifted to ICU.
The patient was treated with 10% 10ml of IV calcium gluconate, nebulised with Salbutamol, 10 units of regular insulin IV combined with dextrose 50%, IV sodium bicarbonate 50 mEq and Inj. Furosemide 40mg IV. Emergent haemodialysis was initiated. Pt was shifted to ICU.