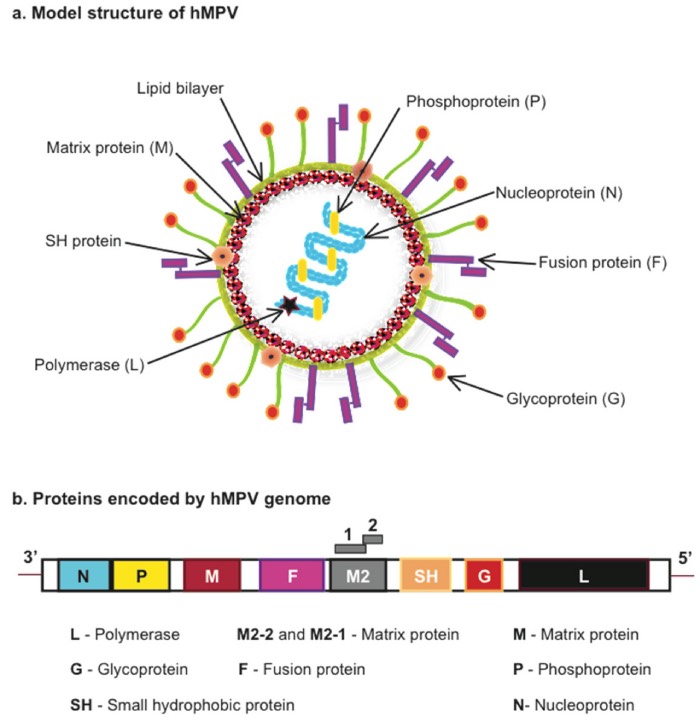
Human metapneumovirus (HMPV) is a negative-sense ss RNA virus of the family Pneumoviridae. It was isolated for the first time in 2001 in the Netherlands. It is the second most common cause after RSV of acute respiratory tract illness.
Subtypes: Four lineages – A1, A2, B1 and B2.
Incubation period: 3-6 days
Transmission: Contact with contaminated secretions, via droplet, aerosol, or hospital acquired infections.
Symptoms: Cough, fever, runny or stuffy nose, sore throat, wheezing, SOB (dyspnea), rash.
Diagnosis: RT-PCR, Immunofluorescence assays, NAAT.
Rx: Supportive care, Ribavirin showed effectiveness in an animal model.
Prognosis: Most people with HMPV have mild URTI similar to the common cold and recover from HMPV in about 7 to 10 days without any complications.
Complications: Viral pneumonia, Bronchiolitis, A/E COPD, secondary bacterial infections.
HMPV outbreak in East Asia began with an outbreak of cases Beijing, China in December 2024. It was linked to 5.4 % of respiratory illness hospitalisations in China, more than COVID-19, rhinovirus or adenovirus. Cases were also reported in Malaysia, India, Pakistan and Kazakhstan.